
A powerful marsquake recorded by NASA’s InSight mission offered scientists their clearest view of the Red Planet’s interior. Seismic waves suggested unusual, dense regions hidden beneath the crust, remnants that some researchers speculate could date back billions of years.
While no peer-reviewed study confirms “Genesis Shards” as an official term, the nickname has surfaced in science discussions to describe hypothetical ancient blocks within Mars’s mantle. What’s certain is that the quake provided a rare seismic snapshot of structures preserved since the planet’s formation.
How It Happened
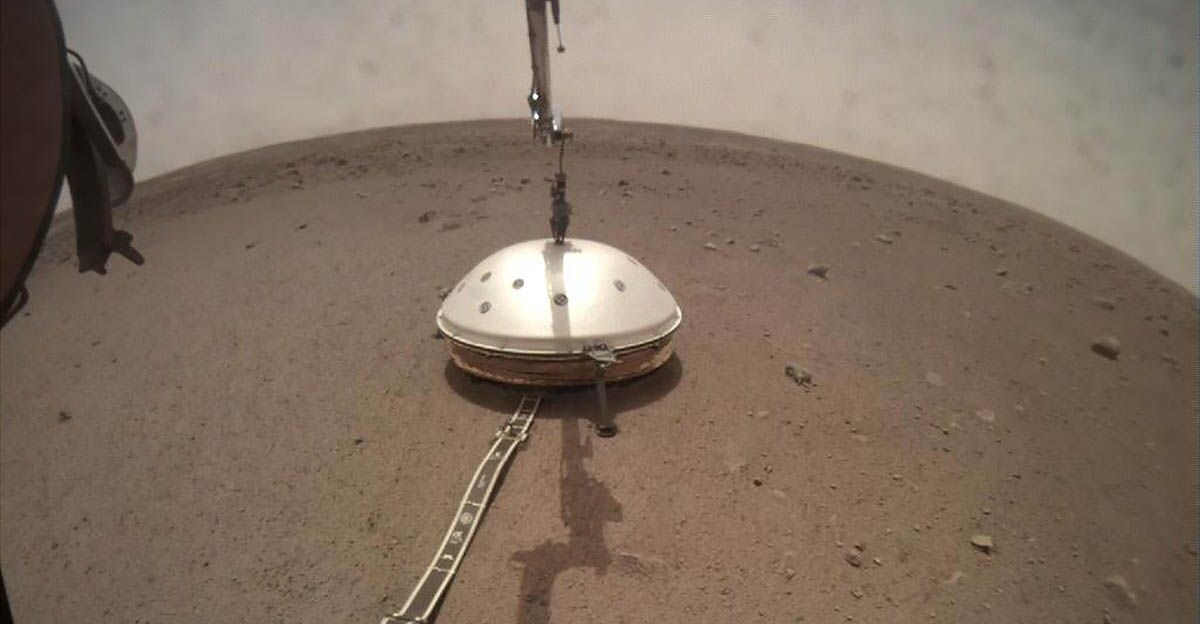

InSight operated on Mars from 2018 to 2022 and carried a highly sensitive seismometer that detected over 1,300 marsquakes. One of the largest, magnitude 4.7, sent seismic waves deep into the planet. Scientists mapped density variations beneath the crust by studying how those waves changed speed and direction.
NASA confirmed that these anomalies reveal layering far deeper than previously understood. Researchers emphasize the signals are real, but what they represent—primordial fragments, mantle heterogeneity, or ancient impact scars—remains open to interpretation.
What Are ‘Genesis Shards’?

The phrase “Genesis Shards” is not from any NASA or Nature paper; it is an informal label used in science writing to describe the possibility that ancient blocks from Mars’s early formation still linger within its mantle. Such material, if confirmed, could act as planetary time capsules.
Mars is unique because it lacks plate tectonics, meaning remnants from its “violent birth” may still be preserved. Scientists agree that mantle anomalies exist, but whether they are truly primordial fragments is a subject of active research, not settled science.
The Role of Marsquakes
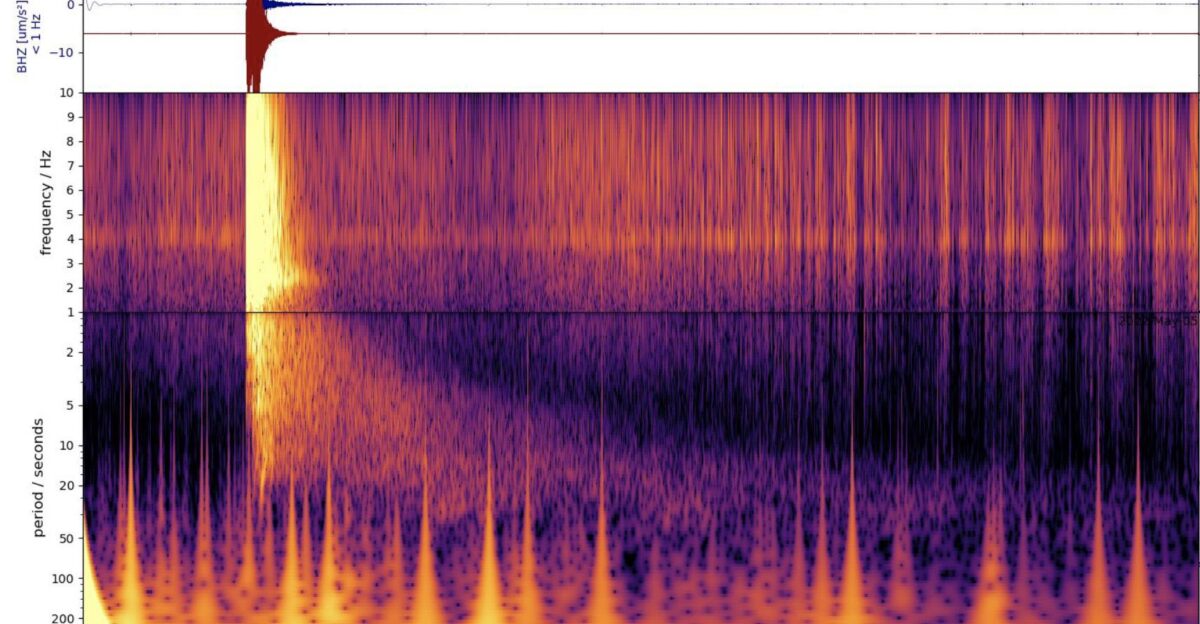
Marsquakes differ from Earth’s quakes because the Red Planet lacks moving tectonic plates. Instead, tremors come from cooling, contracting rocks or asteroid strikes. The May 2022 quake, the largest measured by InSight, was powerful enough to send waves across the planet.
According to NASA, those signals allowed researchers to probe interior structures with unprecedented detail. While headlines sometimes call the anomalies “shards,” planetary scientists stress that interpreting seismic data requires caution. The waves show density contrasts, but what those contrasts mean is still debated.
Why The Findings Matter

The seismic anomalies are essential without a confirmed “Genesis Shards” discovery. They suggest Mars preserved internal structures billions of years ago, features Earth erased through tectonics.
Peer-reviewed papers in Nature showed Mars’s crust and mantle are far less mixed than Earth’s, supporting the idea of a planet that froze early in its evolution. Whether these deep blocks represent fragments from its birth or later impact debris, they make Mars an unparalleled archive of planetary history.
Time Capsule of Ancient Mars

Mars’s geological stillness has long intrigued scientists. Compared to Earth, where plate tectonics constantly recycles rock, Mars retains features from its earliest epochs. That’s why anomalies detected by InSight are so valuable, as they could point to structures dating back over 4 billion years.
“Mars is like a fossil planet,” NASA noted in its 2022 mission summary, emphasizing its potential to preserve conditions from the solar system’s infancy. Any preserved blocks, whatever their origin, offer a rare chance to study processes long erased on Earth.
Violent Origins

Planetary scientists widely agree that Mars, like Earth and the Moon, was pummeled by giant impacts during its first few hundred million years. Some mantle anomalies identified in InSight’s data may stem from that era.
Peer-reviewed Science studies show evidence of heat and melting in the mantle consistent with ancient bombardments. While no team has confirmed that specific blocks of rock survived intact, the possibility remains. The “Genesis Shards” nickname captures the drama of that idea, even if it’s still unproven.
Why They Might Persist
Mars’s lack of tectonic motion means that once material is buried, it often stays buried. That geological “quiet” could allow deep fragments to survive for billions of years. Researchers publishing in Nature Astronomy have argued that Mars preserves a clearer record of early planetary history than Earth or Venus.
Still, no study has verified the exact composition of the anomalies detected by InSight. For now, scientists describe them simply as dense regions inside the mantle, leaving their true origin unresolved.
The Quake That Changed Everything

The May 2022 Marsquake, magnitude 4.7, was strong enough to ripple across the planet. NASA described it as “by far the biggest seismic event” recorded by InSight. The quake’s long-lasting waves gave researchers rare insight into crust and mantle structures.
While media coverage sometimes frames the event as “unearthing” shards, the reality is subtler: InSight’s seismometer translated vibrations into data models, revealing hidden complexity deep underground. What those models represent remains under scientific scrutiny, fueling excitement and caution.
Mapping the Martian Interior

Scientists produced models from the seismic data showing abrupt changes in wave speed at specific depths. These shifts indicate that Mars’s mantle is not uniform; it contains zones with different densities or compositions.
Peer-reviewed results in Nature confirmed a molten layer above the core, surprising researchers who expected a substantial mantle. Whether some of these anomalies are relics of primordial rock or just products of later processes is unknown. The Science remains ongoing, with no official “shard” designation.
Human Scale—If They Exist

If large ancient blocks survive inside Mars, they could be kilometers wide, structures as massive as city districts or small towns. On Earth, plate tectonics would long since have erased such features. Mars’s stillness, however, makes such survival plausible.
While scientists cannot directly observe or sample these anomalies, seismic modeling suggests they could be immense. For readers, the “Genesis Shards” idea is an imaginative way to picture the otherwise abstract anomalies seen in data, though it remains speculative, not proven.
Scientific Reactions

Peer-reviewed findings from InSight have drawn global attention. Researchers hailed the mission for giving “unprecedented detail” about Mars’s crust, mantle, and core in a 2022 NASA press release. But scientists caution against overinterpreting the anomalies.
“We know there are density variations,” one seismologist told Science News, “but whether they’re primordial or not, that’s the big question.” The “Genesis Shards” framing belongs to science communicators, not official studies.
Experts agree that the data is exciting, but the hypothesis of preserved fragments remains unconfirmed.
Clues About Water

One intriguing angle involves water. Analyses of Martian meteorites, like NWA 7034, have shown interaction with liquid water billions of years ago. While InSight cannot directly detect water in mantle blocks, the possibility that ancient anomalies interacted with hydrothermal systems is consistent with other Mars research.
Scientists have proposed that water once circulated deep underground during Mars’s first billion years. This idea connects the anomalies to the bigger question of habitability, though no direct evidence yet links InSight’s seismic signatures to past water activity.
Comparison to Meteorites
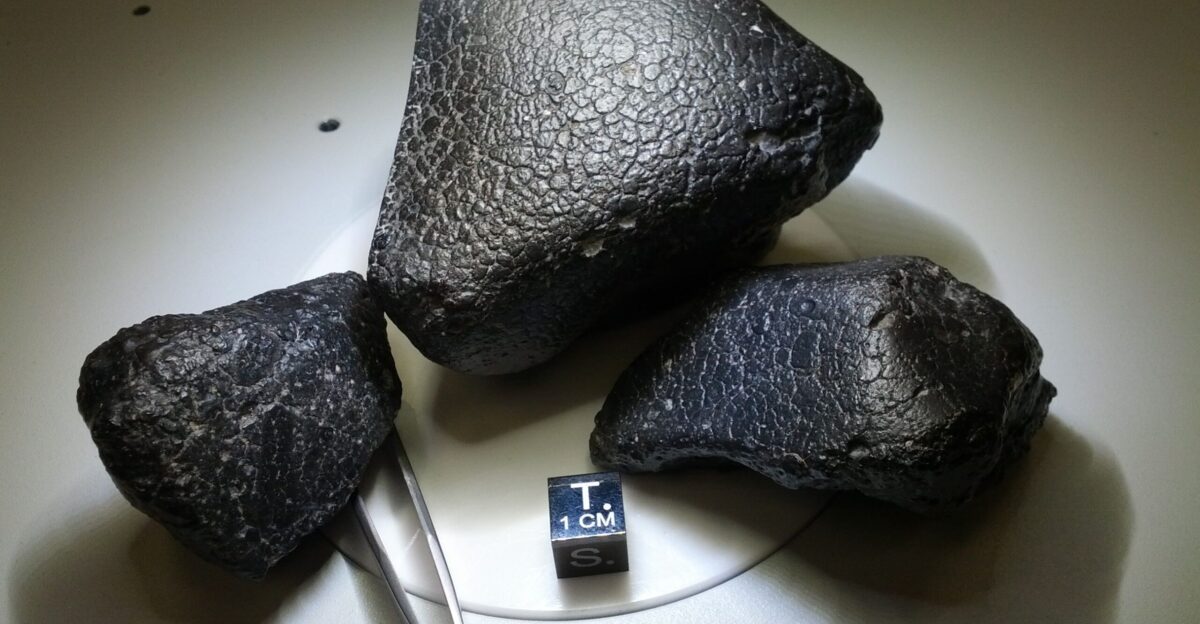

Martian meteorites on Earth, such as ALH84001 and NWA 7034, are genuine 4-billion-year-old samples. They prove that fragments from Mars’s deep past do exist. But those rocks were blasted from the surface and lost their original context.
In contrast, the anomalies detected by InSight are still in place inside the planet. That makes them scientifically valuable, even if their true Nature is debated. The contrast highlights why the “Genesis Shards” idea is so tempting: it combines meteorite evidence with seismic hints from Mars.
A Solid Core—Another Surprise
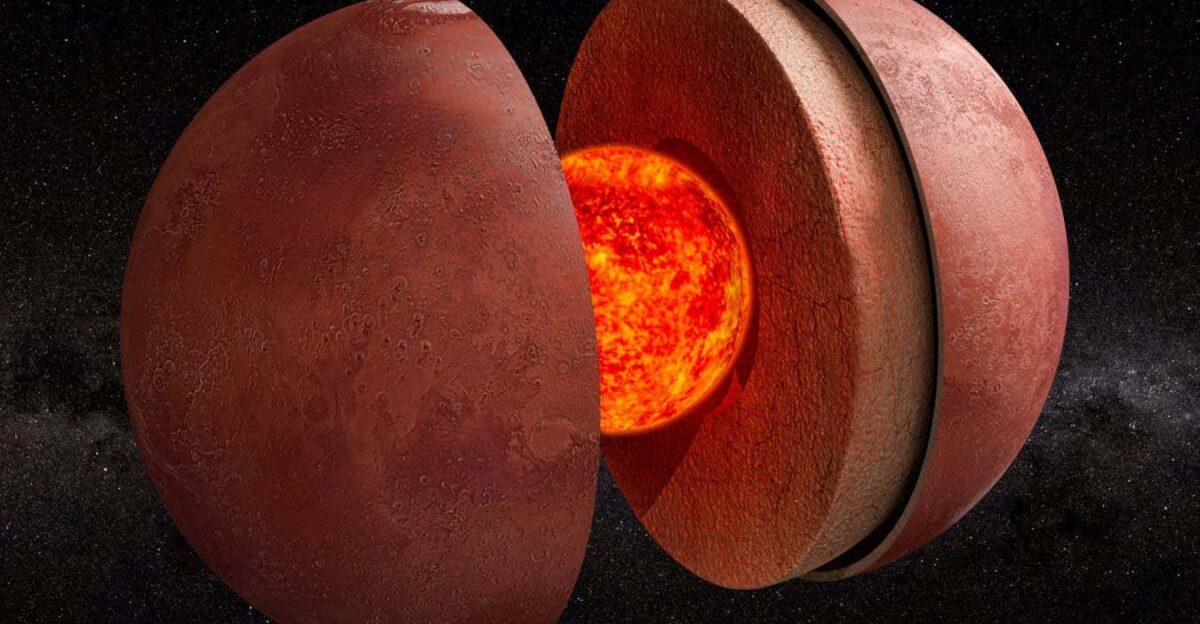
One of InSight’s most robust findings is that Mars has a molten outer core surrounding a smaller solid inner core. This overturned earlier assumptions of a fully liquid interior. Published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the discovery has reshaped theories of Mars’s magnetic history.
The fading of its magnetic field billions of years ago may explain why the planet lost its atmosphere. While not directly tied to the “shards” idea, this confirmed result shows how seismic Science can rewrite textbooks.
Implications for Planetary Science
Whether or not “Genesis Shards” exist, InSight’s discoveries already confirm Mars is a fossil planet, preserving early history that Earth destroyed. For planetary scientists, Mars is a window into conditions all rocky worlds once shared. “Understanding Mars’s interior helps us understand Earth’s origins,” NASA explained in its mission wrap-up.
The anomalies strengthen models suggesting Mars froze early while Earth remained geologically active. Even speculative interpretations highlight the stakes: Mars is central to unraveling why only one rocky planet sustained life.
How The Data Was Gathered
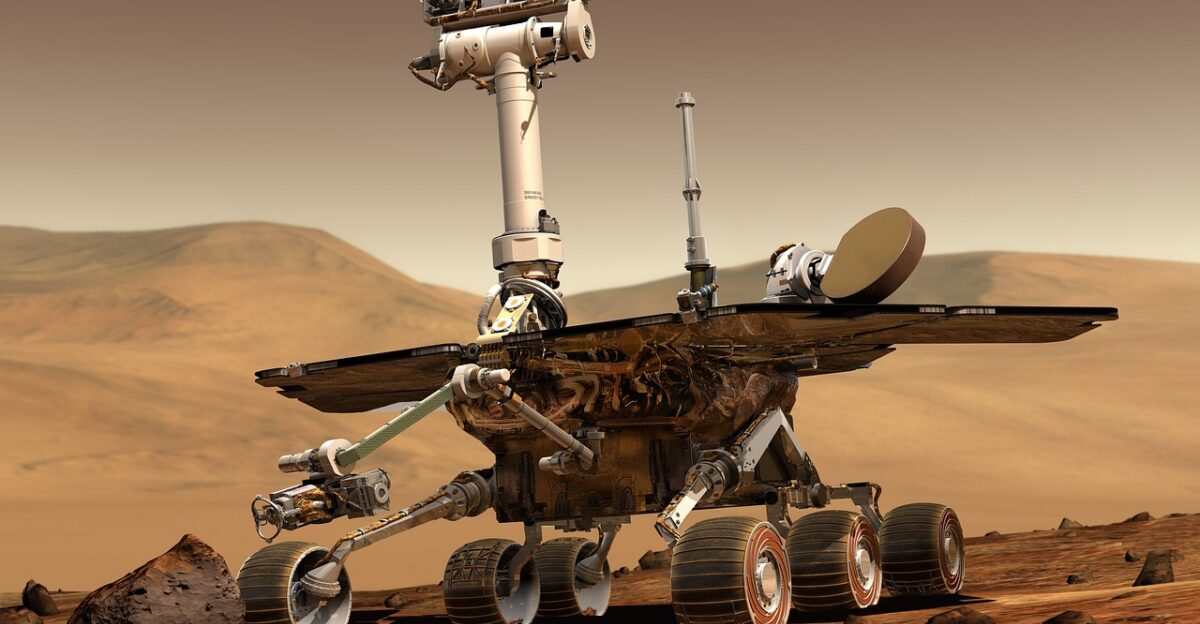

Over four years, InSight recorded more than 1,300 marsquakes before shutting down in December 2022. Dust storms had coated its solar panels, depriving it of power. The data is still being analyzed, with AI tools helping to refine seismic models.
Peer-reviewed papers continue to emerge, showing just how rich the dataset is. NASA emphasized in 2022 that InSight’s legacy will last decades. Any talk of “Genesis Shards” is built on that foundation—speculative storytelling layered onto the mission’s very real, robust Science.
Next Steps—Future Missions
Directly confirming the Nature of mantle anomalies would require new missions. Scientists hope future landers or drills could probe deeper than InSight’s equipment allowed. Another possibility is sample return missions targeting rocks ejected by impacts, which may carry fragments from deep layers.
NASA and ESA have already planned a Mars Sample Return mission, though its focus is on surface material. If anomalies like “Genesis Shards” are ever proven real, it may be through decades of gradual advances in seismology, robotics, and sample science.
Mars—A Living Archive

Regardless of how the anomalies are ultimately interpreted, Mars stands apart as a geologic archive. Its lack of tectonic activity preserved structures billions of years old, frozen snapshots of the solar system’s early days. Each seismic event adds a new piece to that puzzle.
Researchers describe Mars as “holding onto its past” in ways Earth never could. For the public, the “Genesis Shards” idea illustrates this preservation vividly, even if it remains metaphorical. The Red Planet continues to act as a silent witness to cosmic history.
A New Chapter in Martian Exploration

The “Genesis Shards” narrative may be speculative, but the discoveries that inspired it are fundamental. InSight transformed our understanding of Mars’s crust, mantle, and core, proving seismic Science can work on another planet. Its legacy will shape the design of future missions, and its data will fuel debate for years to come.
Whether the anomalies are primordial fragments, impact scars, or something else entirely, they remind us how much remains unknown. Every quake on Mars is not just a tremor but a revelation.